Government incentives and the growing demand for electric vehicles (EV) have led to the introduction of various models that suit the lifestyle of every individual. With a sustainable mobility goal in mind, Sime Darby aims for a 30% reduction of emissions by 2030 and one of the ways we hope to achieve this is to encourage the adoption of EVs.
While you hear most people talk about EVs in general, do you know the different types of EVs available? Here is a guide on the different types of EV.
Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV)
BYD Atto 3
Depending on its battery and capacity of the vehicle, there are three main types of power outputs categorised as Level 1 (slow), Level 2 (fast) or Level 3 (DC Fast Chargers).
Read more about the differences between AC and DC charging at https://www.simedarbymotors.com/about-us/our-stories/what-is-the-difference-between-ac-amp-dc-charging
BEV is the most environmental-friendly electric vehicle, as it operates quietly without an engine and is the most cost-effective in terms of maintenance.
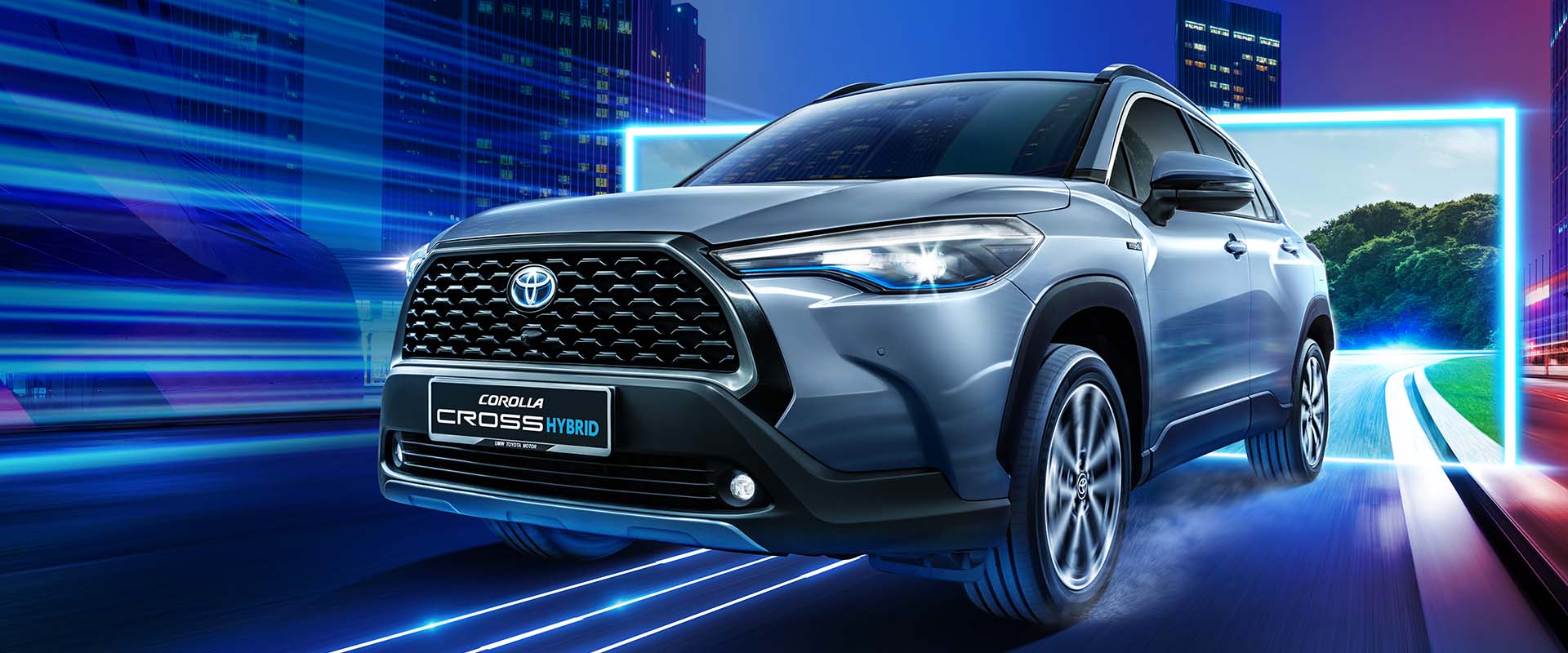
Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV)
Toyota Cross
As its name - Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV), it is powered by both a combustion engine and an electric battery. The combustion engine supports the battery, whereby the vehicle would first consume electricity and later at a certain speed, runs on combustion engine.
A HEV does not offer plug-in or charging sockets to charge its battery. Hence, the battery is recharged when the brake is applied - this process is called “regenerative braking”.
HEVs are fuel-efficient as they reduce consumption of fuel, thanks to the electric battery and are also convenient for long-distance driving, without needing to stop for a recharge.
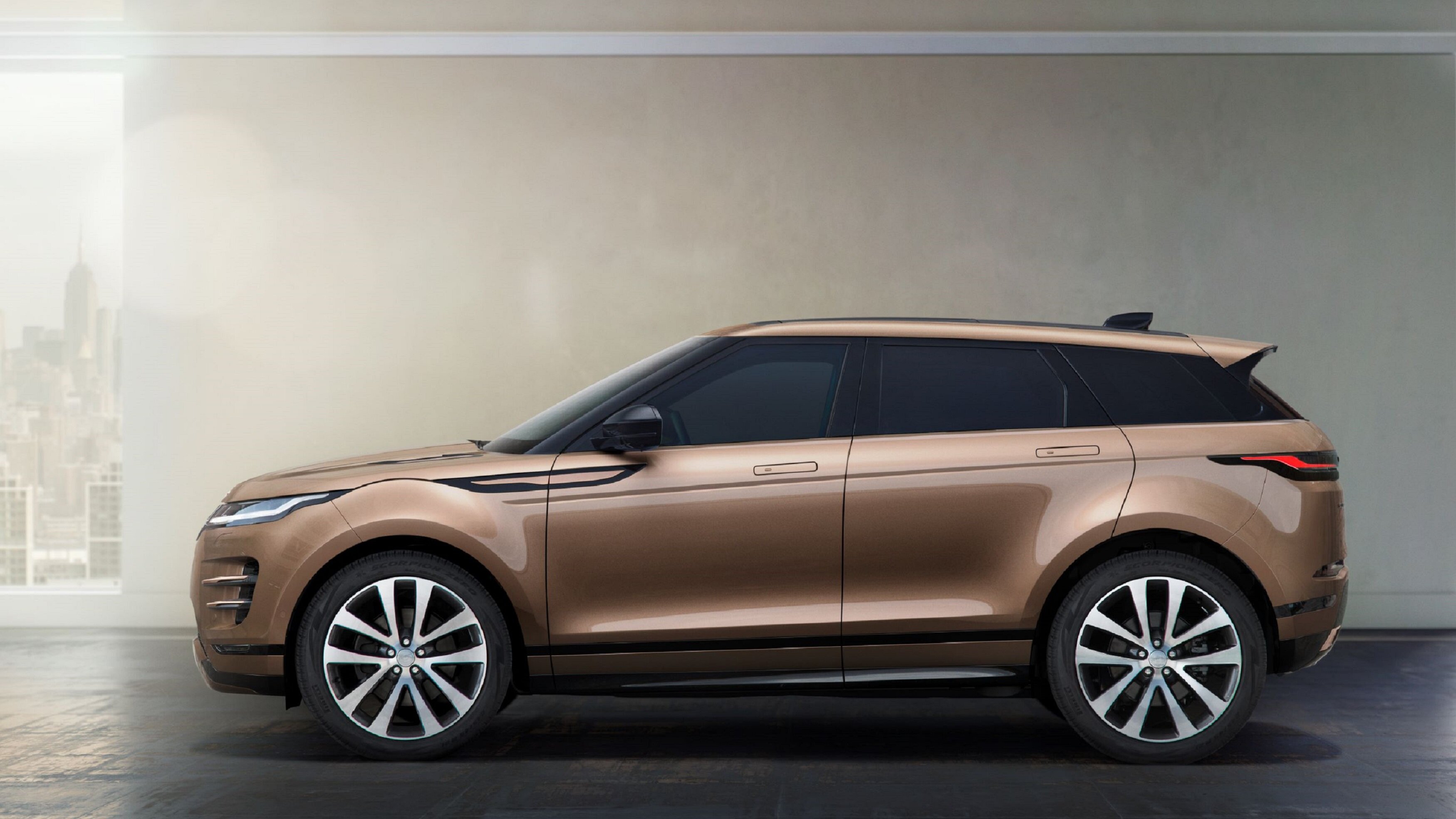
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
Range Rover Evoque